5 Key Factors That Affect Automotive Lighting Mold Costs (Mold Quotation) — Understand the Price Differences
- 邵萱 黃
- Jan 3
- 4 min read

In the automotive lighting industry, the cost of tail light molds can vary significantly—not just due to the size of the part, but more importantly, because of structural complexity, hot runner systems, mold material, and machining difficulty.
In practice, it’s common to see two tail lamps with similar external dimensions, yet the mold cost differs by hundreds of thousands of NTD or even more.
This article explores the five key factors that affect automotive tail light mold pricing from a mold engineering perspective—giving you a clear understanding of the real cost logic behind mold quotations.
5 Key Factors That Affect Automotive Tail Light Mold Costs(
Mold Quotation)
1. More Slides and Side-Cores = Higher Mold Costs
In tail light mold tooling, if the product design includes undercuts, side holes, or hidden snap-fits, then slides or side-core mechanisms are required to complete the injection molding process.
Each additional slide significantly increases the mold cost due to the following reasons:
Each slide requires a dedicated retraction mechanism, often composed of precision-machined components.
It may also need to be paired with lifters, angled pins, or hydraulic cylinders.
Assembly and fine-tuning time increases significantly.
Long-term maintenance and repair costs also rise.
The number of slide units is often the top cost driver in automotive tail light mold quotations.
2. Mold Size in Tail Light Tooling
While mold size generally scales with product size, automotive lighting molds—especially tail light molds—are not solely defined by the external dimensions of the part.
Several practical factors often force an increase in mold size, including:
Slides require longer retraction distances, expanding the mold dimensions.
To protect angled cores, hot runner systems, or delicate components, additional buffer space is added.
Multi-part assemblies require more space for insert configurations and layout.
As mold size increases, so do material costs, machining time, and handling/hoisting expenses.
3. Clear Lens and Light Guide Structures Significantly Increase Mold Cost

In automotive tail light mold development, the clear outer lens and light guide components are often the most expensive and technically demanding parts.
Several factors contribute to this increased cost:
Clear parts require extensive hand polishing, adding both time and labor costs.
Surface quality tolerance is extremely strict, with minimal defect allowance.
Most tail light lenses use valve gate systems for optimized flow control.
Multi-color lens structures (e.g., 2K or 3K molding) dramatically increase mold complexity and cost—each additional material/color adds tooling layers and alignment challenges.
If the product includes high-clarity lenses or precision light guides, mold costs are guaranteed to rise substantially.
4. Fine Texture & Sharp Detailing Increase Machining Cost

Modern automotive tail light designs focus heavily on distinctive styling and fine visual texture—especially on the outer lens and decorative trims.
These high-detail features lead to significantly higher mold manufacturing costs due to:
The need for ultra-fine CNC tooling (small-diameter cutters).
High-speed, low-feed machining strategies to preserve surface fidelity.
Longer machining times to process intricate patterns and textures.
Increased tool wear and frequent replacement during production.
The finer the texture and the sharper the corners, the longer and costlier the CNC mold-making process becomes.
5. Hot Runner System Adds Significant Cost
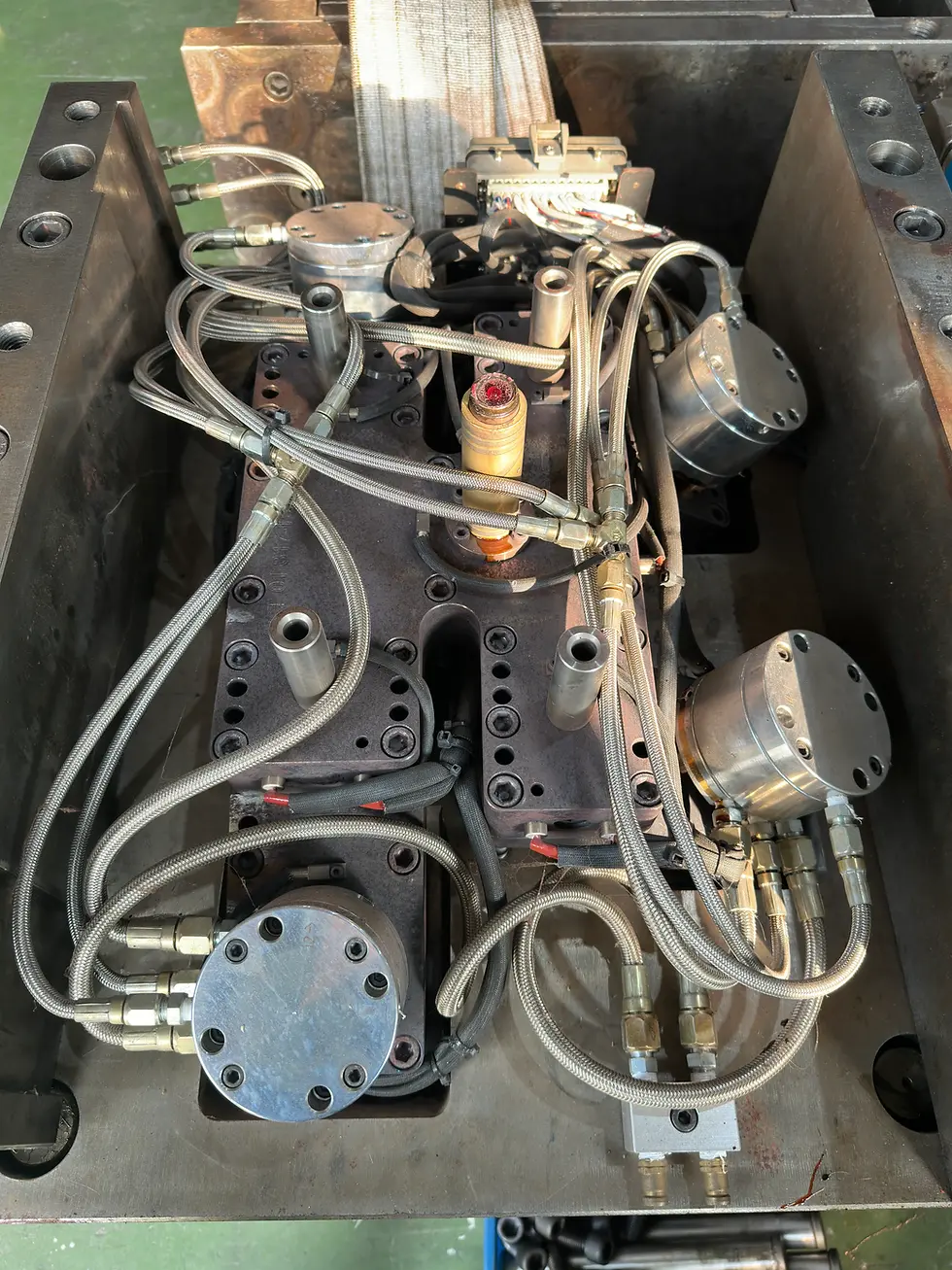
To enhance the appearance and hide gate marks, modern automotive tail light molds often adopt a hot runner systemwith pin-point or valve gate injection.
When a hot runner is used, it introduces extra cost from two key aspects:
Hardware cost: Depends on the brand, number of zones, and valve gate configuration.
Backplate machining cost: Additional tooling is required to accommodate the system, including:
Deep hole drilling for manifold routing
Precision alignment for thermal components
Custom mold base modifications for integration
While a hot runner system improves product quality and reduces post-processing, it is one of the most influential factors behind tail light mold price variation.
Conclusion: Tail Light Mold Costs Reflect Structural and Engineering Decisions
The cost of an automotive tail light mold isn’t simply “high or low”—it reflects a combination of key engineering and design factors, including:
Part structure complexity
Number of slides and core pulls
Transparency and light guide surface quality requirements
Machining precision and surface texture detail
Use of hot runner systems (e.g., valve gate injection)
Choosing a mold manufacturer with hands-on experience in automotive lighting mold development can significantly reduce costs without compromising on quality. By supporting design optimization from the early stages, such partners help streamline the overall mold development process.
Howmin Co., Ltd. specializes in tail light mold engineering and precision machining, with deep expertise in multi-slide structures, transparent and light guide components, and trade-offs in hot runner system and gate design. We work closely with clients at the concept stage to assess structural feasibility, machining complexity, and cost implications—offering practical design improvements that enhance mass production and mold maintenance efficiency.
If you’re planning a new automotive lighting mold project or seeking to minimize trial-and-error and rework costs, we invite you to contact Howmin Co., Ltd.. Our real-world experience can help you achieve a more stable, cost-effective, and production-ready solution.




